
Li Jianzhong, Feng Kai, 306 Hospital of PLA, Special Medical Experimental Research Center
Brand Quality Management Office Zuo Tianyu finishing
In the era of big data, researchers pay more attention to the correlation between the biological information data of the sample and the clinical information of the disease, and predict the occurrence, development and outcome of the disease through the correlation analysis of large samples. The disease biological sample library is the bridge and core of clinical information and sample biological information of related diseases. It is the key source of life science foundation and clinical research. It is the core link for large sample verification and rapid realization of biomedical transformation medicine. In recent years, China's disease biological sample library and translational medicine have received great attention from the government and scientists, hospital leaders and experts have attached great importance to it, and the enterprise and technical departments have strongly supported it. The positive response of the majority of scientific research and medical workers has shown good development. momentum. From the perspective of sample resources, China's biggest feature is the large amount of sample resources and diverse resource types. The number of visits in China for one month may take several months to reach the same number of cases abroad, such as thymic tumors. It is said that the number of cases in Europe is even less than that of a top-three hospital in China. At present, China's biological sample bank has expert libraries, department libraries, multi-disciplinary libraries, major project libraries, hospital libraries, regional libraries, etc. Many hospitals (especially the top three hospitals) have set up their own sample libraries, including boutiques and values. The library, the featured library, and many garbage stores and dead libraries.

Construction of disease biological sample bank
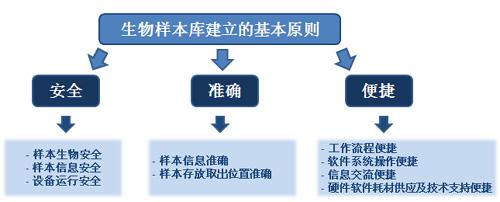
The basic principle of building a sample library is to build a sample library that is safe, accurate, and convenient. Safety includes sample biosafety, sample information security, and equipment operation safety; accurate including accurate sample information, accurate sample storage and removal location; convenient and convenient workflow, convenient operation of software system, convenient information exchange, hardware and software supply and technical support . The sample library usually consists of infrastructure, cryopreservation equipment, cryo-consumable supplies, coding and reading equipment, monitoring equipment, management software and staffing. A reasonable architecture and process can ensure that the sample library runs safely, accurately and conveniently.
infrastructure
The infrastructure generally includes quality inspection room, sample processing room, refrigerator room, liquid nitrogen equipment room, monitoring room, air conditioning equipment, backup power supply and so on. It should be noted that the refrigerator is a heat generating device and needs to be placed separately from the liquid nitrogen device. Vertical refrigerators can be placed back to back at a certain distance if they cannot be placed against the wall. Considering that the ultra-low temperature refrigerator is still the main storage device of the tissue bank, it will generate a large amount of heat during the operation, and the power and performance reliability of the sample library should be given sufficient consideration when equipped with the sample library air conditioner. Backup power is also a basic feature of the sample library. In areas where power supply is not sufficiently stable, the temperature insulation of the refrigerator (ie, the rate at which the temperature rises after a power failure at full load) is taken into consideration when selecting a refrigerator. When the sample size is large enough, you also need to consider the equipment that uses automated pick and place samples. For particularly important samples, backups of samples can be placed separately at different physical locations for increased safety if conditions permit.

Basic equipment
(1)-800C cryopreservation equipment (ultra-low temperature refrigerator): The temperature of stable operation of ultra-low temperature refrigerator is usually around -800C, and it is easy to rise to the recrystallization temperature range of -600C when taking samples, which is easy to cause the attenuation of biological stability of the sample. Therefore, the cooling capacity (speed) is a key parameter when using an ultra-low temperature refrigerator. Refrigerators with high cooling capacity can be temperature-disturbed and quickly drop to a set temperature to minimize damage to the sample. In addition, because the purpose of the sample library is to store samples for a long time, ultra-low temperature refrigerators need to run uninterrupted for many years under full load conditions, and their reliability and temperature stability are higher than those of ordinary laboratories. The refrigerator in the sample library requires a continuous recording function of the operating temperature to track temperature fluctuations.

(2)-1400C cryopreservation equipment (liquid nitrogen phase and deep-cooling refrigerator): liquid nitrogen phase and deep-cooled refrigerator are common equipment for realizing -1400C long-term sample storage. In both cases, there is no risk of liquid nitrogen entering the sample, so there is no risk of cross-infection between samples during storage. The cryogenic refrigerator is a relatively new type of equipment. From the feedback of customers in recent years, it can achieve a stable environment of -140~-1500C with full load of samples, and more and more applications have been obtained. The liquid nitrogen phase is a more widely accepted method, and the liquid nitrogen phase is recommended for long-term storage of tissue samples in the sample library operating specification documents of the National Cancer Institute and other institutions. The liquid nitrogen phase is a certain amount of liquid nitrogen added to the liquid nitrogen container, and the sample is stored in a space in the container that is not in direct contact with liquid nitrogen. The temperature in the gas phase zone of the liquid nitrogen container is the lowest (at the mouth of the vessel) not higher than -1400C. A small amount of sample can be stored in a liquid nitrogen tank. The liquid nitrogen tank that fits the cryobox is used to consume a larger amount of liquid nitrogen, but the sample is convenient to take and put, and the sample is not easy to fall into the liquid nitrogen tank. More and more users of liquid nitrogen tanks have adopted this type of configuration. A large number of samples have higher requirements for the convenience of handling and liquid nitrogen filling, and currently mainly use liquid nitrogen storage tanks. Automatic liquid nitrogen detection equipment and automatic filling equipment are usually required, including liquid nitrogen supply tanks, liquid nitrogen towers and liquid nitrogen pipelines.

(3)-1960C cryopreservation equipment (liquid nitrogen tank and liquid nitrogen storage tank): The liquid nitrogen liquid phase can maintain the sample at a low temperature of -1960C, which is the best sample storage temperature that can be achieved under the current technical conditions. Compared with the liquid nitrogen phase, the liquid nitrogen liquid phase is easier to implement, and the liquid nitrogen container can be filled with liquid nitrogen to store more samples, but the requirements for consumables such as cryotubes containing samples are higher. The blood bag of cryopreserved hematopoietic stem cells can be stored directly in liquid nitrogen, but the cryotube can not be directly stored in liquid nitrogen, and needs to be treated. It is required to use a cryotube sleeve to seal the whole body of the cryotube. The method requires a higher freezer box and a larger interval of freeze shelves. An easy way is to use a sealing film to seal the joint between the cryotube cap and the body. Some common 10x10 bottom spacers are compatible and do not require special cryotubes. From the current customer response and literature, this method is simple, but the effect is relatively reliable.

Monitoring equipment
Monitoring equipment includes refrigerator temperature probe, refrigerator operating temperature record, liquid nitrogen container liquid level monitoring, remote alarm, video monitoring and so on. Ultra-low temperature refrigerators and deep-cooled refrigerators require real-time monitoring of temperature. Although many manufacturers have temperature measurement and data output devices on the equipment, many users choose to install a temperature probe to monitor the temperature separately. The position of the temperature probe is recommended to be placed in the bottom area of ​​the refrigerator with the highest temperature to ensure sample safety. The operating temperature record of the refrigerator is also a basic requirement. Remote alarm system currently uses mobile phone alarms combined with network alarms. The temperature detecting device will automatically alarm the relevant manager's mobile phone SMS through the SIM card pre-made in the refrigerator and other devices through the alarm in the normal temperature range, and the related information will also alarm to the management software system through the Internet or the data line. In recent years, video surveillance has gradually become the routine configuration of many laboratories. In addition to the installation of conventional camera monitoring in corridors, exits, etc., high-resolution cameras with adjustable focal lengths can be remotely monitored and recorded in key operation steps such as sample processing and freezing. Whether the operator's operation details are standardized or not is very helpful for strengthening personnel management to ensure sample quality.
Other equipment
The sample library usually requires a certain sample transport and transfer. -200C sample transfer is generally done with a cold pack (Gel pack), -700C with dry ice, and below -1500C with a liquid nitrogen transport tank. To avoid delays in package delivery due to accidental reasons, a minimum of 24 hours of refrigerant allowance is required in the sample package. The frozen storage pipe rack directly affects the storage capacity of the container sample, and the type of the root frozen storage device and the consumable material needs to be specifically selected or customized. A library with a particularly large sample size may also use an automated access device. This solution is currently only used with the -800C device and requires a specific management software to freeze the device.
All samples derived from humans are considered to be potentially infectious and harmful and must be tested by the relevant pathogens and processed accordingly. Sample handling must be performed in a biosafety cabinet. Biosafety cabinets provide simultaneous cleanliness of the sample as well as the operator and the environment, but the wind from the clean bench is blown from the inside out, protecting the cleanliness of the sample and protecting the operator and the environment from potential pathogens. Hazard.
Frozen storage supplies
Compared with the general laboratory, the sample library has a longer sample storage time, stricter protection requirements for the stability and integrity of various components in the sample, and a larger number of uses, so the performance characteristics and specifications of the consumables are selected higher. Requirements.
At present, the sample storage consumables commonly used in the sample library are 1~5 ml cryotubes, of which 2 ml cryotubes are the most commonly used. Some manufacturers label the cryotubes with actual capacity of 2 ml and 5 ml as 1.8 ml and 4.5 ml working capacity to remind the user not to fill up, to prevent liquid freezing is the increase in volume and damage the seal. In addition to the conventional single-use cryotubes, there are also cryotubes that are stored in a 96-well plate format, using specially designed shapes and caps for automated robotic arm operation.
Polypropylene is the most commonly used for making polypropylene (PP) because it can withstand low temperatures (-1960C), has relatively low liquid nitrogen permeability and good chemical resistance (such as DMSO). Cryotubes. As a substance that is directly in contact with the sample during storage of the biological sample, the reliability level of the raw material directly affects the safety of the loaded substance. The grade of polypropylene material can be judged from four aspects: purity, sterility, chemical tolerance and adsorption to biomolecules (cells, proteins, RNA and DNA, etc.).
The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) classifies plastic grades into six grades. Among them, grade 6 plastics require multiple cell-contacting tests to ensure that they are least toxic to cells and can be used in the preparation of medical device products. Therefore, it is recommended to use the plastic cryotube as the ultra-pure medical grade original resin in the sample storage and pass the USP Class VI test. The adsorption of bio-macromolecules by cryotubes during long-term storage is an important consideration. For blood samples, especially purified micro-macromolecule samples, ordinary plastic pipes are prone to decrease in the concentration of certain biomacromolecules in the sample due to adsorption during long-term storage, which destroys the integrity of the sample. Therefore, it is recommended to use a dedicated and reliable cryotube in the sample library. It is not recommended to use non-special consumables such as microcentrifuge tubes. In addition, in order to better maintain the long-term tightness, the National Cancer Society Organization Library recommends the use of a cryotube with a thread seal. It is not recommended to use plug-in or pop-up consumables. The spiral of the cryotube has internal and external rotations. The external rotation is designed for ultra-low temperature refrigerators. The internal rotation is designed for lower temperatures such as liquid nitrogen or cryogenic refrigerators. However, direct storage of the cryotubes in liquid nitrogen requires further protection of the cryotubes to prevent leakage of liquid nitrogen. Leakage of liquid nitrogen into the cryotube is not only easy to cause the cryotube to explode and destroy the sample during thawing, and endangers the operator. The more serious consequence is the cross infection between the samples. The sterility of the cryotubes is also an important indicator, especially for samples that may be used for clinical use in the future, as close as possible to or close to the 2010 new Chinese Pharmacopoeia requirements for consumables (SAL 10-6).
For some larger samples, Nalgene currently has a 15ml wide-mouth sterile cryotube for 5-15ml of liquid or large tissue storage. Blood bags can be used for larger fluid volumes. The wide-mouth sterile cryotube and blood bag can withstand the low temperature of -1960C.
Sample management information
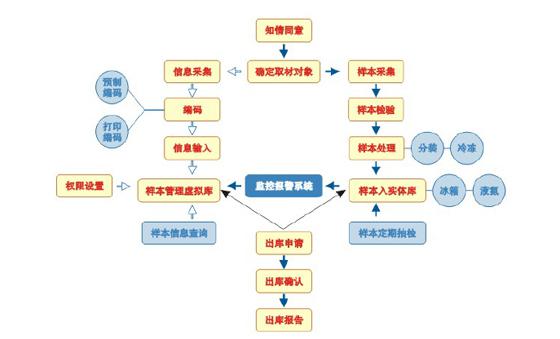
It is difficult to meet the large-capacity cryopreservation needs of the sample library by the cryotubes of the handwritten markers in the general laboratory. A common solution is to edit and print one- or two-dimensional code and sample information on-site and then manually paste it onto a common cryotube. Another solution is to choose a manufacturer to laser etch a two-dimensional coded cryotube. The two schemes are compared from the perspectives of identification and robustness of the code. The advantages of the latter scheme in practical application are obvious and the current development direction. The consumable cost of the preset two-dimensional code is higher than the on-site print coding scheme as a whole, but the print coding scheme has special requirements for label paper, print quality, and adhesive, and needs to withstand long-term low temperature storage and a certain humidity. Ordinary printing paper and ordinary ink are prone to label peeling, illegible writing and ink costs such as lead and other contaminated samples. These additional costs can even be comparable to the price of a common cryotube and need to be fully considered when making budgets. The paper-based cryopreservation box is a cryopreservation box used in the early days of ordinary laboratories and has been replaced by polycarbonate cryopreservation boxes in recent years, especially at temperatures below -1400C. The library requires higher reliability than the general laboratory. It is recommended to use a polycarbonate cryobox. Some polycarbonate freezers can be autoclaved if needed. Some standard size polycarbonate freezer boxes can be used to place 10x10 2 ml or less external or internal coils with a bottom cylindrical spacing. The spacing of the same externally sized paper freezer box can usually only be placed in 9X9 2 ml external or internal spiral storage tubes.
In the case of a large potential sample size of the sample library, two-dimensional coding is required, and the prefabricated two-dimensional coding exhibits an irreplaceable advantage. Firstly, the two-dimensional code printed on the paper label has a low recognition rate after long-term freezing, so the currently used one-dimensional and two-dimensional hybrid print-encoded labels actually rely mainly on one-bit coding to provide reliable identification. Secondly, the pre-fabricated two-dimensional coding tube can realize fast reading, and can better meet the high-throughput requirements of the sample library. The pre-made two-dimensional code is stored in a 96-well plate storage format (SBS footprint), and all the cryotubes on the whole plate can be read from the bottom at one time using an automated code reader, thus minimizing sampling time and reading reading. Damage caused by temperature rise during sampling.
Because different sample libraries have large differences in coding and reading equipment, monitoring equipment, refrigeration equipment, consumables, sample capacity, etc., management software is usually tailored according to the user's specific configuration and requirements, and in some cases, Integration with other management software in the lab and further improvements based on requirements and feedback in later use. Since the management software, equipment, and consumable coding equipment are an overall system, system compatibility should be considered when selecting software. Software integration of monitoring equipment, alarm equipment, interface friendliness, scalability and stability are also important considerations. In addition, the management software needs to set management rights for the sample information to ensure the privacy of the sample source. The management software is provided by the equipment/consumer manufacturer, and is provided by a third-party software company, and a sample library is also produced according to its own needs.
As an important resource in the era of big data, the database of disease biological samples is of great significance for the study of the occurrence, development, prognosis and treatment of diseases. Achieving quality management of sample libraries, structural data structure and standardized data sharing will be three key tasks in the construction of the sample database in the era of big data. Among them, the quality management of disease biological samples and their information will determine and influence the results of the research. Therefore, to achieve the quality management system of disease biological samples and related quality testing methods, to achieve continuous improvement of the quality of the sample library, will contribute to the development of disease research.
Corn Seed,Seed Corn,Maize Seed,Sweet Corn Seeds
XIKE AGRICULTURAL GROUP CO . .LTD. , https://www.laoseed.com