

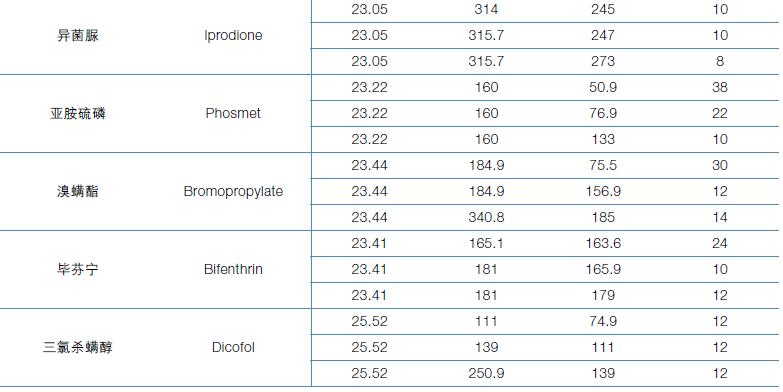
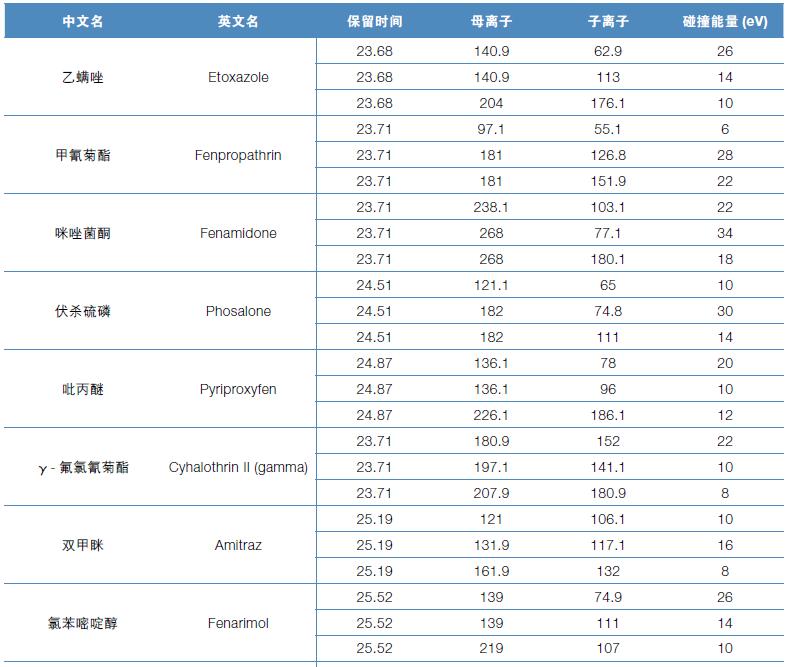
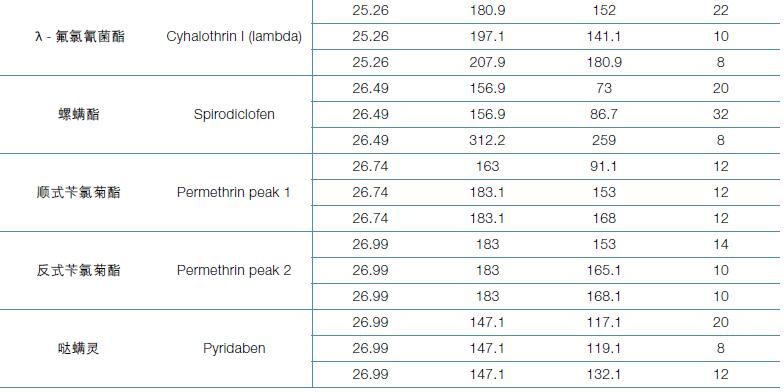
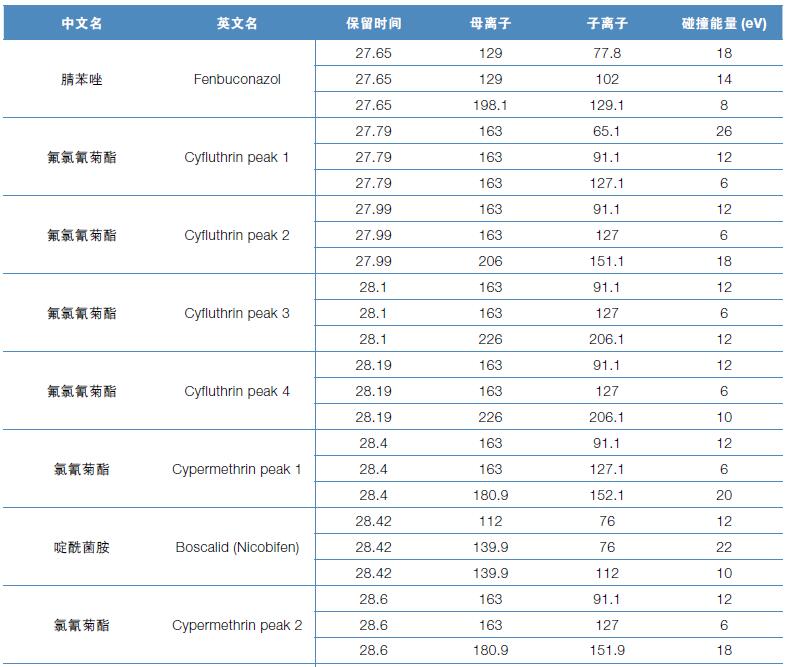
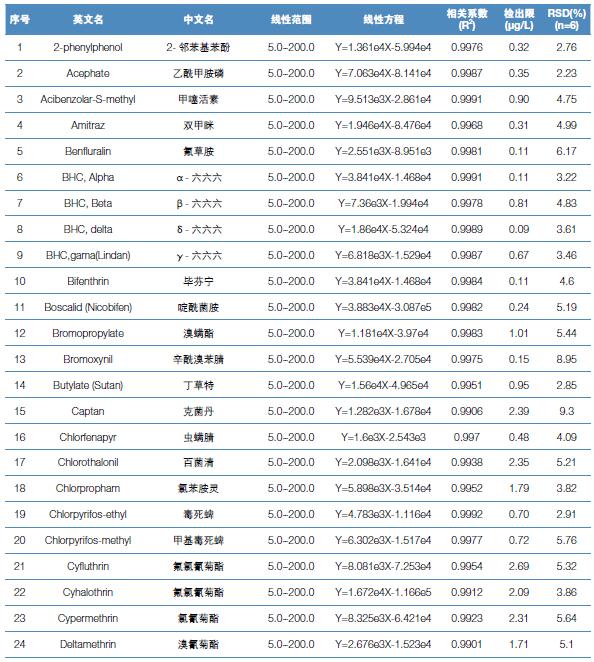
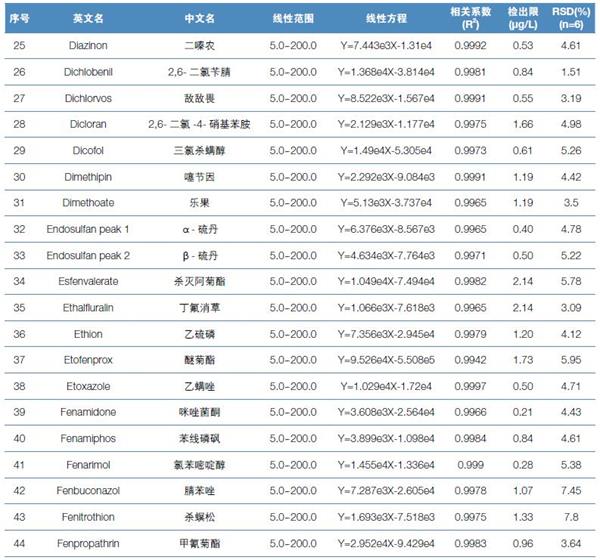
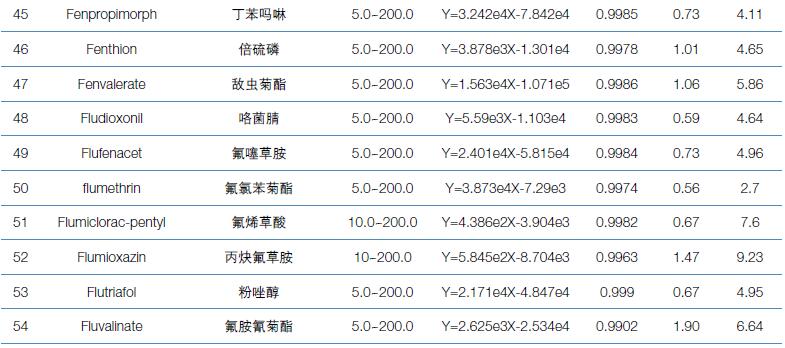
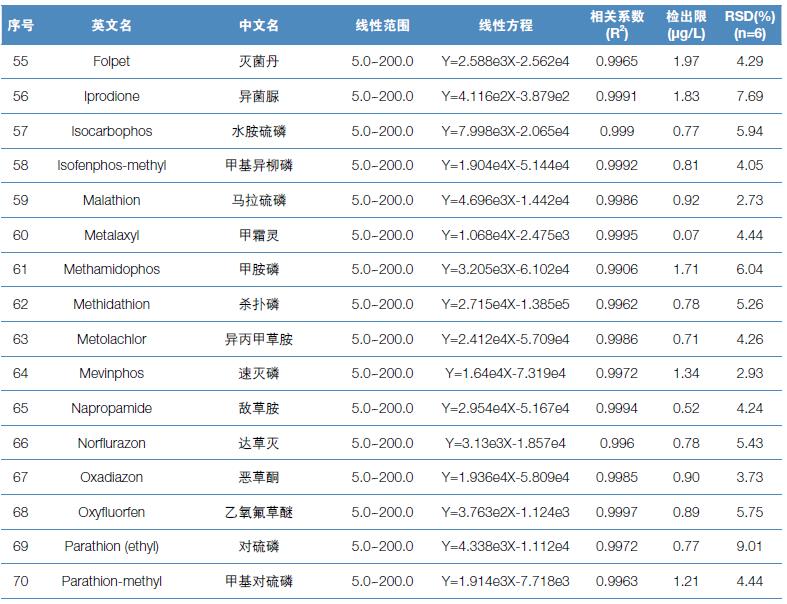
Hematology analyzer is also called clinical blood cell analyzer, blood cell analyzer, blood cell analyzer, blood cell counter. The blood analyzer not only improves the accuracy of the experimental results, but also provides many experimental indicators, which play an important role in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of diseases. Hematology analyzer is one of the most widely used instruments in hospital clinical testing.
Test items
Blood cell test refers to routine blood test, which is manual operation and counting under the microscope at first. It includes red blood cell, hemoglobin, white blood cell count and its classification, platelet count, etc. There are more than 20 items.
clinical significance
1. The blood analyzer is mainly used to detect various blood cell counts, white blood cell classification and hemoglobin content.
2. Hematocrit: obtained by multiplying the average volume of red blood cells by the red blood cell count.
3. Red blood cell distribution width: represents the degree of consistency of red blood cell size. When the red blood cell size is uneven, the red blood cell distribution width value increases, such as various types of nutritional deficiency anemia.
4. The three average indices of red blood cells are used to identify the type of anemia.
(1) The average hemoglobin content of red blood cells: increased in megaloblastic anemia, decreased in iron deficiency anemia, chronic blood loss anemia, uremia, chronic inflammation.
(2) Mean volume of red blood cells: increase in hemolytic anemia and megaloblastic anemia; decrease in severe iron deficiency anemia and hereditary spherocytosis.
(3) The average red blood cell hemoglobin concentration: decrease in chronic blood loss anemia, iron deficiency anemia; various diseases can be in the normal range. In megaloblastic anemia, the mean red blood cell volume increases, the mean red blood cell hemoglobin amount increases, the mean red blood cell hemoglobin concentration is normal, and the red blood cell distribution width increases.
5. Average platelet volume: the average volume of each platelet, the size of platelets is related to its function.
(1) Increased: seen in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, edema and proteinuria in late pregnancy.
(2) Decreased: seen in non-immune platelet destruction, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia repeated infection syndrome, chronic myeloid leukemia, etc.
Automation in Hematology,Automated Hematology Analyzer,Hematology Analyzer Instrument,Hematology Analyzer Product
Jilin Sinoscience Technology Co. LTD , https://www.jlgkscience.com