Professor Wang Meiqing from the School of Stomatology and Military Stomatology, Fourth Military Medical University, and the team of Professor Xiao Guozhi from the Department of Biology, Southern University of Science and Technology, used a model of flow fluid shear stress (FFSS) in cultured chondrocytes. The unilateral anterior crossbite (UAC) animal model found that both FFSS and UAC can actively induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in the temporomandibular joint chondrocytes, demonstrating that abnormal mechanical load can be activated by activation of the temporomandibular joint cartilage. The MTORC1 signal in autophagy and apoptosis programs leads to cartilage degeneration, a feature published in Autophagy, suggesting that inhibition of MTORC1 may be a new strategy for the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis.
The temporomandibular joint is a joint that connects the mandible to the skull (sacral) and is located deep in front of the ear canal. Temporomandibular arthritis (temporal jaw arthritis, temporomandibular joint disorder syndrome) is a joint pain caused by a variety of causes. It can also cause headache, neck pain, facial pain, ear pain, temporomandibular joint interlocking, difficulty in occlusion or temporomandibular joints. The cause of the disease is complex and is not fully understood.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic degenerative joint disease that destroys articular cartilage and has high socioeconomic costs. Biomechanical factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of OA. The temporomandibular joint is biomechanically related to occlusion and is a site often invaded by OA. Professor Wang Meiqing previously reported that fluid shear stress (FFSS) can induce choroidal articular chondrocyte death in vitro. Subsequently, they established an abnormal occlusal mouse model called unilateral anterior cross (UAC) and demonstrated that mechanical stress can also induce temporomandibular joint chondrocyte death and OA-like damage in rats and mice.
In the new study, they combined the research group of Professor Xiao Guozhi from the Department of Biology of Southern University of Science and Technology to study the molecular mechanism of abnormal biomechanical induction of chondrocyte death and temporomandibular joint OA.
Based on the previously established model, the researchers first monitored the cartilage area of ​​the sham-operated group and the UAC group for 2 to 20 weeks, while quantifying caspase-specific protease 12 (CASP12) and DNA damage induces expression of autophagy molecules such as transcript 3 (DDIT3) as well as the location of autophagosomes and lysosomes.
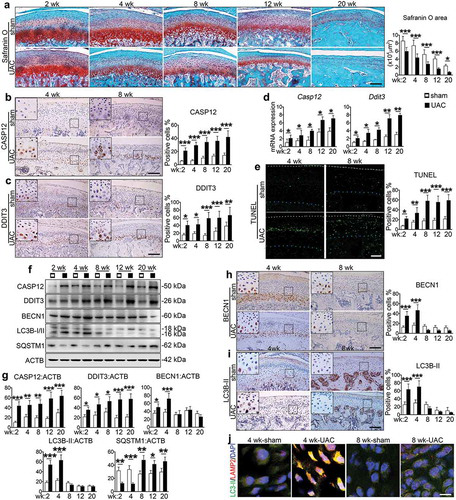
Endoplasmic reticulum stress response (ERS) was present in the temporomandibular joint chondrocytes throughout the UAC experiment. However, it is worth noting that the endoplasmic reticulum core signal 1 (p-ERN1) increases only in 2 to 4 weeks, and after 8 weeks, both mRNA and protein will reach normal normal levels. During this period, UAC induced down-regulation of chondrocyte p-MTOR and its downstream target p-RPS6 for 2 to 4 weeks. That is, UAC induces ERS apoptosis in the OA process, promoting autophagy in the early stage and autophagy in the late stage. As a well-known autophagy inhibitor, MTORC1 was inhibited at an early stage and activated in the late stage, suggesting that it plays a key role in the transformation of autophagy into ERS apoptosis in the progression of UAC-induced temporomandibular joint OA cartilage.
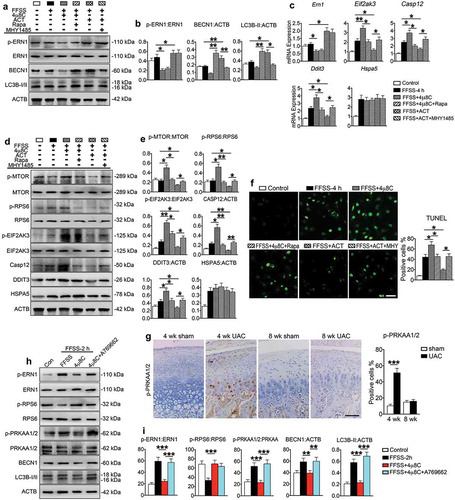
In the same way, they demonstrated that FFSS stimulates ERS apoptosis in cultured ATDC5 cells, activates autophagy in early stage and inactivates MTORC1, and activates MTORC1 to inhibit autophagy in the late stage.
To further investigate the role of ERN1 in the regulation of MTORC1 during ERS apoptosis and autophagy, ATDC5 cells are infected with ERN1 expressing lentivirus ( providing viral packaging services by Saiye Bio ) and are effective in the presence of MHY1485 (mTOR agonist) Accepted for 4 hours of FFSS under conditions of inhibition of autophagy) and absence of MHY1485. The results showed that overexpression of ERN1 inhibited p-MTOR and p-RPS6, up-regulated BECN1 and LC3B-II, promoted autophagy of chondrocytes, and at the same time, down-regulated p-EIF2AK3, CASP12 and DDIT3, inhibited induction by FFSS Chondrocyte apoptosis. MHY1485 can reverse the inhibition of ERN1 expression on p-MTOR and p-RPS6, thereby inhibiting autophagy and promoting ERS apoptosis.
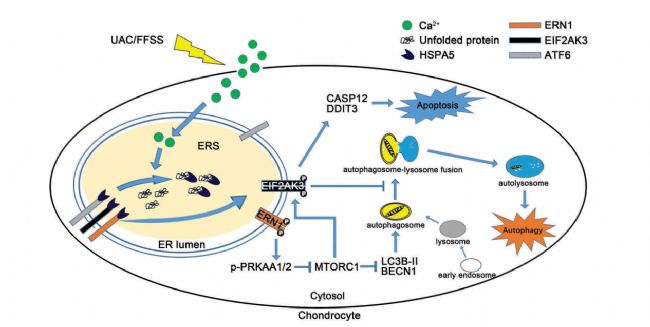
In summary, the FFSS and UAC models established by the researchers elucidated the interaction between MTORC1 in ERS cell apoptosis and autophagy flux. Mechanical stress promotes ERS by up-regulating p-EIF2AK3 and p-ERN1, and ERN1-MTORC1 signaling is initiated. Ventilation flux induces ERS apoptosis in chondrocytes. MTORC1 is located downstream of p-ERN1-AMPK and transforms autophagy into chondrocyte ERS apoptosis by up-regulating p-EIF2AK3 in response to sustained abnormal biomechanical conformity, thereby promoting the expression of CASP12 and DDIT3, ultimately leading to apoptosis (see below). Show).
Original search: MTORC1 coordinates the autophagy and apoptosis signaling in articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritic temporomandibular joint
Ultrasonic Spot Welding Machine
Product categories of Plastic Ultrasonic Spot Welding Machine, we are specialized manufacturers from China,Portable Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine, Digital Ultrasonic Spot Welder suppliers/factory, wholesale high-quality machine of ultrasonic Spot welding R & D and manufacturing, we have the perfect after-sales service and technical support. Look forward to your cooperation!
Ultrasonic Spot Welding Machine,Portable Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine,Ultrasonic Spot Welding Machine For Mask,Digital Ultrasonic Spot Welder
Wuxi DIZO Ultrasonic Technology Company , https://www.dizosonic.com